Using Gas-Removing Tubes for Infants: A Guide

Intro
The use of a gas-removing tube for infants can be a necessary intervention in certain situations. Parents and caregivers may find themselves in a position where they must relieve their infant from discomfort caused by gas buildup. Understanding the ins and outs of this process is crucial for ensuring both effectiveness and safety.
One must consider various factors, including the proper application technique and necessary safety measures. This comprehensive guide aims to elucidate these critical points while also discussing potential complications that may arise. Establishing this knowledge not only empowers parents but also significantly contributes to the well-being of the child.
Обзор продукта
Gas-removing tubes are specialized medical devices designed to alleviate excessive gas in infants. Their primary function is to provide a pathway for gas to exit the body, thereby relieving discomfort and preventing more severe complications.
Характеристики и преимущества
- Design: These tubes are typically flexible and soft, reducing the risk of injury during insertion.
- Size: They are specifically manufactured for infants, ensuring proper fit and effectiveness.
- Usage: Easy to use, most gas-removing tubes come with clear instructions that detail application processes.
- Immediate Relief: Many parents report quick results in providing comfort to their infants after using these tubes, promoting better sleep and feeding.
Недостатки и ограничения
- Risk of Injury: Inappropriate use can result in damage to delicate tissues if caution is not observed.
- Not Suitable for All Cases: Gas-removing tubes may not be appropriate for severe medical conditions, necessitating an evaluation by healthcare professionals.
- Dependency: Over-reliance on this method may prevent parents from addressing underlying issues related to gas buildup.
Безопасность и качество
When using a gas-removing tube, safety and quality are paramount. Understanding the materials involved and adhering to recommended guidelines can mitigate associated risks.
Материалы и их влияние на здоровье
The materials used in the construction of gas-removing tubes should prioritize an infant's safety. Non-toxic materials such as silicone or soft plastics are generally preferred. Parents must verify that the tube is free from harmful chemicals that could pose risks to their child's health.
Рекомендации по безопасности при использовании
- Always sanitize the tube before use to prevent infection.
- Consider the correct size to avoid injury during insertion.
- Monitor the infant closely during and after the procedure to ensure no adverse reactions occur.
- Consult with a pediatrician for guidance, especially if the infant has pre-existing health conditions.
"Proper knowledge and technique are essential when it comes to using a gas-removing tube for infants. Never hesitate to reach out to a medical professional for guidance."
Preamble to Gas-Removing Tubes
Using a gas-removing tube can be a necessary measure for infants suffering from excessive gas. This guide aims to elucidate the various aspects related to gas-removing tubes, ensuring that parents and caregivers can use them safely and effectively. Knowledge about the topic is essential, as improper use may lead to discomfort or complicate the situation.
Understanding Digestion in Infants
Infants undergo a unique digestive process, which is often less efficient compared to older children and adults. The infant's gastrointestinal system is still developing, leading to common issues like gas accumulation. Gas can arise from multiple sources, such as swallowed air during feeding or digestion of certain foods. This build-up can lead to discomfort, making it crucial for caregivers to understand how to alleviate these symptoms. Understanding how digestion works in infants sets the foundation for why gas-removing tubes may be needed. The timing, type of feedings, and position of the baby can all have an impact on their digestive comfort.
The Role of Gas-Removing Tubes
Gas-removing tubes serve a specific purpose: to provide relief from gas that may cause pain or irritability in infants. These tubes, usually made of flexible and soft material, are designed to help expel excess gas from the digestive tract. When inserted correctly, they allow for the release of trapped gas, offering immediate relief to the infant. Educating caregivers on the operation and function of these tubes is vital. The method of insertion, along with knowledge of the infant's reaction, directly influences the success of the procedure. Proper understanding can minimize risks and enhance the overall well-being of the infant during this common but distressing issue.
Types of Gas-Removing Tubes
When addressing gastrointestinal discomfort in infants, understanding the types of gas-removing tubes available is essential. These tubes serve various purposes and are designed with specific features to enhance the comfort of the infant while ensuring ease of use for parents and caregivers. The selection of the appropriate type can influence both the effectiveness and safety of the procedure. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing the experience.
Material Considerations
The materials used in gas-removing tubes significantly impact their effectiveness and safety. Common materials include medical-grade silicone, rubber, and plastic. Each material has its own benefits and drawbacks.
- Medical-grade silicone is flexible and gentle. It is less likely to cause irritation, making it suitable for delicate skin.
- Rubber can provide better grip during insertion but may be harder to clean.
- Plastic is rigid but lightweight, often leading to easier storage.
It's vital to ensure that any material used is free from harmful chemicals. Parents should look for products that explicitly mention they are latex-free and BPA-free. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines on material safety to avoid any potential risks.


Sizes and Shapes
Gas-removing tubes come in various sizes and shapes, which can affect their usability and comfort for the infant. The choice of size is particularly important, as it must correspond to the infant's age and weight.
- Standard Sizes: Different manufacturers provide tubes in specific sizes, commonly measured in French sizes (Fr). A common range for infant tubes is from 5 Fr to 12 Fr. Smaller sizes are usually for newborns, while larger ones may be appropriate for toddlers.
- Shape Variations: Some tubes are straight, while others might be slightly curved. A straight tube generally allows for easier insertion, but a slightly bent shape could help with maneuverability during use.
When selecting a tube, it is crucial to consider the individual needs of the infant. Keeping size and shape in mind, along with the potential for comfort, can significantly enhance the experience for both the infant and the caregiver.
Selecting the right tube type reduces discomfort and promotes safe usage.
Preparing for the Procedure
Preparing for the procedure of using a gas-removing tube is crucial for ensuring both the safety and comfort of the infant. This process involves careful planning and consideration of various elements. The aim is to gather all necessary supplies and to create a suitable environment. Ensuring proper preparation can minimize discomfort for the infant and promote a successful experience for caregivers.
Gathering Necessary Supplies
Before starting the procedure, it is essential to have all necessary supplies ready. Having these items on hand can make the process smoother and more efficient. Supplies that should be gathered include:
- Gas-removing tube: Ensure it is the appropriate size and material suitable for the infant’s age and weight.
- Lubricant: A water-soluble lubricant can ease insertion and minimize discomfort.
- Clean cloth or towel: To keep the area clean and dry, as well as to handle any mess that may occur during the procedure.
- Access to a change of clothes: In case of any accidents, it is practical to have spare clothing available.
- Disposable gloves: To maintain hygiene during the procedure.
- Suction device: Depending on the circumstance, some parents may find it useful to have this ready for any additional gas expulsion needs.
- Infant thermometer: To check the infant’s temperature before and after the process, in case of any concerns.
Having these items not only equips the caregiver for the procedure but also promotes a confidence that benefits the infant's experience.
Creating a Comfortable Environment
An infant’s comfort is vital during any medical procedure, including the use of a gas-removing tube. A calm and reassuring atmosphere can significantly impact how the infant responds. Here are some practical steps to create a comfortable environment:
- Choose a quiet space: Select a location free from distractions, where the infant can feel secure.
- Regulate the temperature: Ensure the room is at a comfortable temperature. A too hot or too cold environment can make an infant more irritable.
- Gentle lighting: Use soft lighting to avoid startling the infant. A dimmed room can help create a soothing atmosphere.
- Comfort items: If the infant has a favorite blanket or toy, having these nearby can provide reassurance.
- Calm demeanor: Caregivers should maintain a calm and composed attitude. Infants are sensitive to their caregivers’ emotions, so staying relaxed can help the infant feel more at ease.
By focusing on these elements, caregivers enhance the likelihood of a successful gas removal procedure, offering peace of mind to both the infant and the guardian.
Proper preparation is key to ensuring a successful and safe experience with a gas-removing tube. Having the right supplies and environment in place can make all the difference.
Step-by-Step Instructions
The process of using a gas-removing tube for infants is sensitive and requires careful execution. Each step is important, as any mistake can cause discomfort or complications. Understanding the step-by-step instructions helps empower parents and caregivers. This guide ensures a safe and effective approach, minimizing the risk of errors during the procedure. Adhering to these instructions gives peace of mind, knowing that you follow a proper method.
Positioning the Infant
Proper positioning is the first step in the process of using a gas-removing tube. The infant should be placed on their back on a flat, comfortable surface. A changing table or a soft blanket on the floor can work well. It is crucial to support the baby's head and neck, keeping them stable. This position helps in reducing discomfort during the procedure. It also allows easy access to the area where the tube will be inserted. Make sure the surroundings are calm and quiet, as a relaxed environment can ease the infant’s anxiety.
Additionally, use cushions or rolled towels to support the infant’s sides. This can prevent any unexpected movements that might complicate the procedure. If possible, have another adult present to assist. They can help to gently hold the infant in place or provide reassurance.
Proper Insertion Technique
The insertion technique is key to successfully using a gas-removing tube. Before starting, ensure that the tube is clean and free of any obstructions. Lubricate the tip of the tube with a small amount of sterile lubricant to ease the insertion.
Begin by gently inserting the tube into the infant's rectum. Insert it about one inch deep. Do not force the tube; if you experience resistance, pause and gently wiggle it. Apply steady, gentle pressure, while monitoring the infant's reaction. If the baby seems to be in pain, stop immediately.
Once the tube is in place, you may need to hold it for a few seconds to allow the gas to escape. It is important to watch closely for any signs of distress. The baby's comfort should always be a priority during this step of the process.
Monitoring Comfort Levels
After the insertion, monitoring the infant’s comfort is crucial. Look for physical signs such as squirming, crying, or tense body movements. These may indicate discomfort or distress. If the infant displays any signs of discomfort, remove the tube immediately and try to soothe them.
Pay attention to the infant's breathing patterns and heart rate as well. Any irregularities can suggest that the infant is not coping well with the procedure. If you notice any unusual signs, do not hesitate to seek medical assistance.
Establishing a connection with the baby during this time can be helpful. Talk softly or sing gently to maintain a sense of calm. This can improve their overall experience.
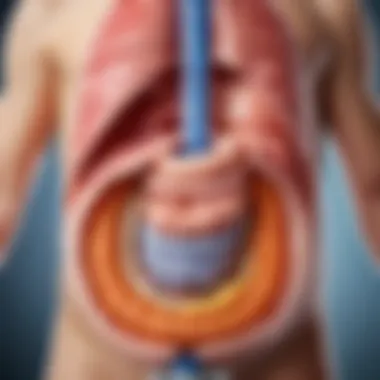

Using a gas-removing tube can be beneficial for relieving discomfort caused by gas. Following these step-by-step instructions ensures a higher level of safety and effectiveness. Always prioritize the well-being of the infant.
"Always be attentive to your infant's reactions during the process; their comfort is paramount."
Post-Procedure Care
Post-procedure care plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of the use of a gas-removing tube for infants. After the technique is completed, it is important to maintain a clean and safe environment for both the infant and the caregiver. Proper aftercare can help prevent infections, ensure the infant's comfort, and identify any potential issues early. This section focuses on two main aspects of post-procedure care: cleaning the area and recognizing signs of complications.
Cleaning the Area
Following the use of a gas-removing tube, careful cleaning is essential. It is important to clean the area around the insertion site to minimize the risk of infection. Here are some steps to follow:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before attending to the infant. Use hand sanitizer if soap and water are not available.
- Use mild soap and warm water to clean the insertion area. Avoid harsh chemicals that may irritate the sensitive skin of the infant.
- Gently pat the area dry using a soft cloth or a tissue. Do not rub the area as this can cause discomfort.
- Apply a protective ointment as recommended by a pediatrician to help soothe the skin and form a barrier against bacteria.
- Ensure the diaper and surrounding clothing are clean and dry to avoid any further irritation.
Regular cleaning should continue for a few days following the procedure. Parents should observe the area for any signs of redness or swelling.
Signs of Complications
Recognizing early signs of complications is vital in ensuring the infant’s well-being after using a gas-removing tube. While most procedures go smoothly, there are instances where complications can arise. Here are key signs to watch for:
- Excessive crying or fussiness beyond the normal level can be indicative of discomfort or distress.
- Swelling or redness around the insertion site may signal an infection or irritation.
- Fever can indicate a possible infection. This is a serious condition and should be addressed promptly.
- Vomiting or signs of nausea need to be reported immediately as they might indicate a more serious issue.
If any of these signs appear, seeking professional help is essential. Monitoring the infant after the procedure is just as important as the procedure itself. Equipping parents with the knowledge about post-procedure care can lead to safer outcomes and improved comfort for the infant.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Understanding the potential risks and limitations associated with the use of gas-removing tubes is crucial for parents and caregivers. While these devices can provide relief for infants experiencing discomfort from gas, they are not without concerns. Knowing these risks enhances the ability to use gas-removing tubes effectively and safely.
Identifying Risks
Several risks can accompany the use of gas-removing tubes. First, improper insertion can lead to physical trauma if done without care. It's essential to ensure that the tube is inserted gently and to the appropriate depth. Additionally, there may be a risk of causing colicky reactions if the gas is released too rapidly from the intestines. This can lead to greater discomfort for the infant, which can increase the distress levels during the procedure.
Infection is another risk when using gas-removing tubes. Maintaining proper hygiene is vital. Before and after using the tube, clean hands and ensure that the device is sanitized. Ignoring these steps can introduce bacteria leading to infection. Always monitor the infant for any signs of redness or swelling around the insertion site.
Furthermore, some infants may experience discomfort from the tube itself. If a parent notices resistance or crying that seems excessive during insertion, it is important to stop and reassess the approach. If a risk seems apparent or the infant does not appear to tolerate the procedure, it is better to avoid using the tube entirely.
When to Seek Help
Knowing when to seek assistance from a healthcare professional is equally important in ensuring that the use of a gas-removing tube does not lead to complications. If an infant shows continuing signs of distress after using the tube, it may be time to consult a pediatrician. Persistent crying, refusal to eat, or other atypical behaviors warrant attention.
In certain cases, if there are any unusual symptoms such as unusual swelling, bleeding around the insertion area, or if the infant becomes unusually lethargic, parents should seek immediate medical assistance.
It is always better to err on the side of caution. Discussing concerns with a pediatrician prior to using a gas-removing tube can also provide valuable insight into the specific needs of the infant. Having a professional guide through the process can alleviate risks and provide peace of mind to caregivers.
In summary, understanding the potential risks and indicators for when to seek help can greatly reduce complications while promoting the safe use of gas-removing tubes for infants.
Alternative Solutions for Gas Relief
Gas discomfort in infants can be a challenging issue for parents and caregivers. While gas-removing tubes serve as a valuable tool in providing immediate relief, exploring alternative solutions can enhance overall comfort for the infant. These methods can be used in tandem with more invasive techniques, ultimately promoting well-being without the associated risks.
Dietary Adjustments
Dietary changes can play a significant role in managing gas in infants. It's essential to monitor what your baby consumes if they are formula-fed or gaining nutrients through breast milk. Certain ingredients can contribute to increased gas production. For example, if you are breastfeeding, consider evaluating your own diet to see if you consume dairy products, beans, or cruciferous vegetables, as these can also affect the infant through your milk.
For formula-fed infants, exploring different formulas can be beneficial. There are specialized formula types designed to be easier on the digestive system, such as hypoallergenic or lactose-free options. Parents might want to experiment with these options under pediatric guidance.


It's also wise to introduce new foods gradually, if the infant is at the appropriate age for solid foods. Watching how your baby reacts to each introduction can help pinpoint problematic foods.
Dietary adjustments may alleviate gas discomfort and improve digestive health for infants.
Gentle Massage Techniques
Gentle massage is another effective method for relieving gas in infants. This technique can improve gastrointestinal function and promote relaxation. A parent or caregiver can use their hands to apply gentle pressure to the infant's abdomen, aiding in the breakdown of gas bubbles.
Start by holding the baby comfortably, ensuring they feel secure. Use your fingers to gently stroke the belly in a clockwise direction, following the natural movement of the intestines. This is not only soothing but can also stimulate digestion.
Additionally, leg bicycles can also assist in relieving gas. By gently moving the baby's legs in a cycling motion, caregivers can encourage the release of trapped air. This technique requires minimal effort and can easily be incorporated into daily routines.
Both dietary changes and gentle massage techniques offer complementary solutions to using a gas-removing tube, providing a holistic approach to infant gas relief.
Consulting with Pediatricians
When it comes to the health and well-being of infants, consulting with pediatricians is crucial. These medical professionals have specialized training that equips them to handle various infant health concerns, including the use of gas-removing tubes. The guidance they provide can be invaluable, making the journey smoother and more secure for caregivers.
Using a gas-removing tube is not a routine process; it requires knowledge and skill. Parents may worry about using the tube correctly or about potential complications. By collaborating with a pediatrician, caregivers can gain insights tailored to their child’s unique needs. They can also receive personalized advice on the signs to look for, post-procedure care, and how to manage any discomfort their infant may experience.
Furthermore, pediatricians can help dispel myths and clarify misunderstandings surrounding the use of gas-removing tubes. Having a professional's backing can alleviate anxiety and bolster confidence in the process.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Professional guidance helps in optimizing safety and effectiveness when using gas-removing tubes. Pediatricians are trained to explain the underlying causes of gas issues in infants. Knowing the reason behind the gas can inform the proper use of the tube.
Additionally, the pediatrician can introduce alternative solutions or therapies. This comprehensive perspective is vital; caregivers should not rely solely on tubes for gas relief. A pediatrician can guide parents through a range of options, ensuring a well-rounded approach is taken.
Another significant point is the importance of follow-up consultations. Pediatricians can monitor progress and ensure any treatment is effective. They can also modify the approach as necessary, responding to changes in the infant's condition.
Overall, the connection with a pediatrician contributes to informed decision-making, enhancing the effectiveness of care provided to the infant.
Questions to Ask Your Pediatrician
When consulting with a pediatrician about using a gas-removing tube, it is essential to prepare a list of questions. This can help clarify processes, expectations, and concerns. Here are some important questions to consider:
- What signs should I look for before using a gas-removing tube? Understanding the signals that indicate your infant is experiencing discomfort can help determine when to take action.
- Are there any specific techniques I should follow? Details about the correct methods for insertion and use are crucial to lessen risks.
- What should I observe post-procedure? Knowing what to watch for after using the tube can help in recognizing potential complications early.
- Are there any products you recommend? Some tubes may be more suitable than others, so professional insight can make a difference.
- When should I consider alternative treatments? Learning when to pivot to different methods can expand your toolkit for addressing gas issues.
By engaging in this dialogue, caregivers can gain confidence in their approach, ensuring the infant’s needs are met appropriately.
Final Considerations
The considerations outlined in this section are crucial for ensuring not only the effectiveness of using a gas-removing tube but also the overall well-being of the infant involved. Understanding and respecting the unique needs of infants plays a significant role in how parents and caregivers approach this task. This method, while effective, requires careful thought and reflection to balance immediate relief with long-term health impacts.
Understanding Infant Needs
Infants have distinct needs that differ significantly from older children and adults. Their physical and emotional well-being is deeply interconnected. When using a gas-removing tube, one must prioritize the infant's comfort and safety.
The first step involves developing a strong awareness of the baby’s cues. Infants may not be able to articulate discomfort, yet their expressions, movements, and sounds can be strong indicators of how they are feeling. Often, they may squirm, cry, or show signs of distress, which can signal discomfort related to gas build-up. Recognizing these cues can help guide the caregiver’s response, making it essential to remain attentive throughout the procedure.
Additionally, the environment plays a pivotal role in an infant's response. A warm, quiet space tends to soothe babies, while a stressful setting may exacerbate their discomfort. Thus, creating a calm atmosphere can enhance a smoother application of the gas-removing tube, making both the infant and caregiver feel more at ease.
Reassessing the Method
After using a gas-removing tube, it is crucial to reassess the method applied. This requires a thoughtful evaluation of the entire process. Consider factors such as the infant’s response to the procedure and whether there were any signs of discomfort or complications.
If the proposed method seems ineffective or causes distress, it may be necessary to explore alternatives. Consulting healthcare professionals can also provide reassurance and clarity. Effective communication with pediatricians can shed light on whether the current technique is suitable or if adjustments are needed.
Regularly checking in on the infant’s condition post-procedure not only promotes safety but encourages informed decision-making about future actions and adaptations.
Moreover, parents and caregivers should keep a log of experiences during each procedure. This log can highlight patterns over time, helping identify what works best for their particular infant. Analyzing these records can facilitate proactive adjustments to technique, improving outcomes and reducing anxiety for both infants and caregivers.
Ultimately, final considerations are not just about concluding a procedure but laying the groundwork for future care and support. With the right approach, every step taken can contribute to a healthier and more responsive infant caregiving experience.







